You will not become an expert in one course
Topics
- 基本的神经网络
- MLPs
- Convolutional networks
- Recurrent networks
- Boltzmann machines
- 一些高级的网络
- Generative models: VAEs
- Adversarial models: GANs
- 课程中涉及到的一些topics
- Computer vision: recognizing images
- Text processing: modeling and generating language
- Machine translation: Sequence to sequence modeling
- Modelling distributions and generating data
- Reinforcement learning and games
- Speech recognition
Perceptron
本章节的前面部分主要是讲解的一些历史的发展,感兴趣可以翻看课件。下面主要从Perceptron开始。先上数学表达式:
$$p_i=
\begin{cases}
1& \text{$if \sum_i w_ix_i-T>0$}\
0& \text{$else$}\
\end{cases}$$
Perceptron的学习策略为:
$$w=w+\eta(d(x)-y(x))x$$
- $d(x)$ 是label
- $y(x)$ 是感知机的输出
其实现可以参考percptron,感知机网络的几个特点如下
- Boolean tasks
- 当输出为错误的时候更新参数
- 针对于线性可分的数据证明是可以收敛的(机器学习基石中有证明)
如图所示,感知机可以很容易的用来模拟布尔运算(这里的输入是0或1不是实数,后面会介绍实数),其中边上的值是权重,圈里面的值是阈值,对应上面的数学表达式。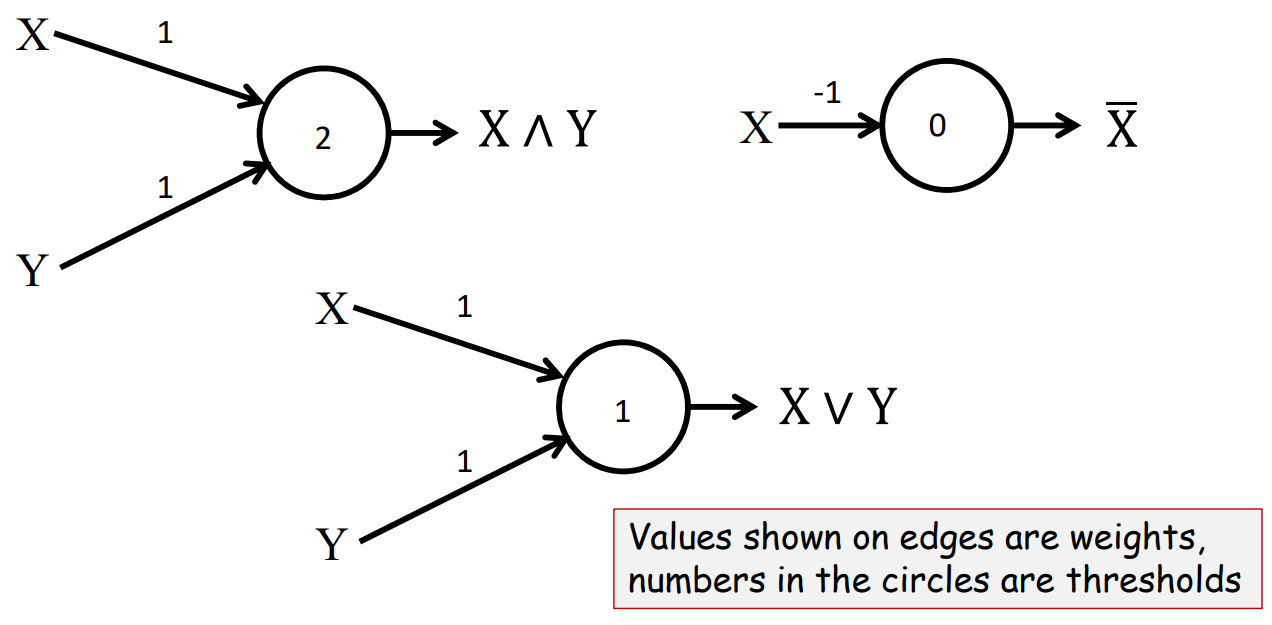
如图感知机可以表示与或非,但是不能表示异或。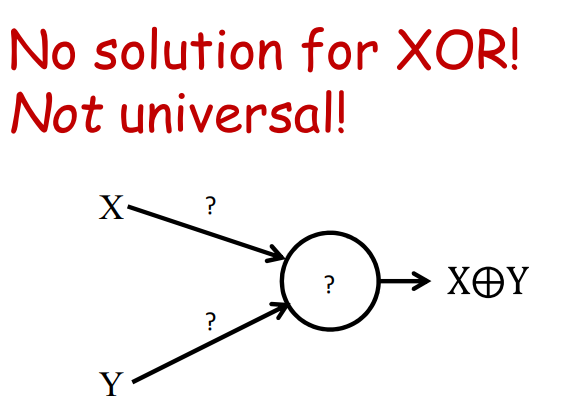
A single neuron is not enough
所以由上面的例子可以得到的结论是一个单一的神经元是不能够用来表达异或的,表达能力有限
- Individual elements are weak computational elements
- $\color{orange}{Networked}$ $\color{orange}{elements}$ are required
所以提出了多层感知机的模型。如图的多层感知机可以用来表示异或
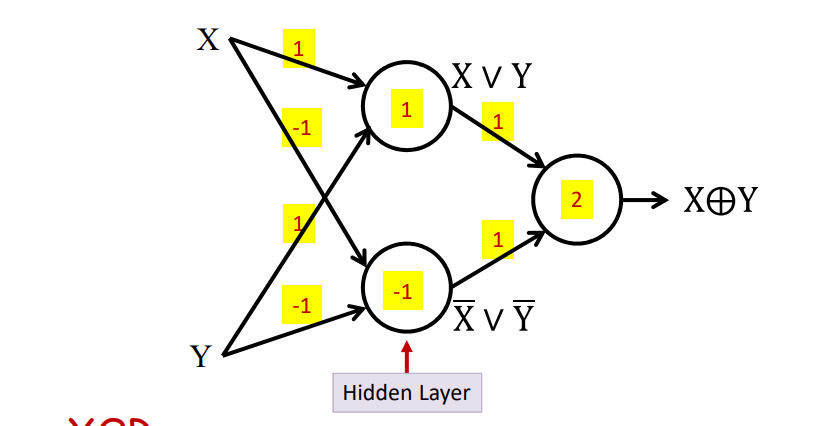
其中第一层是隐藏层。下面列举了一个更加一般的例子,如图。
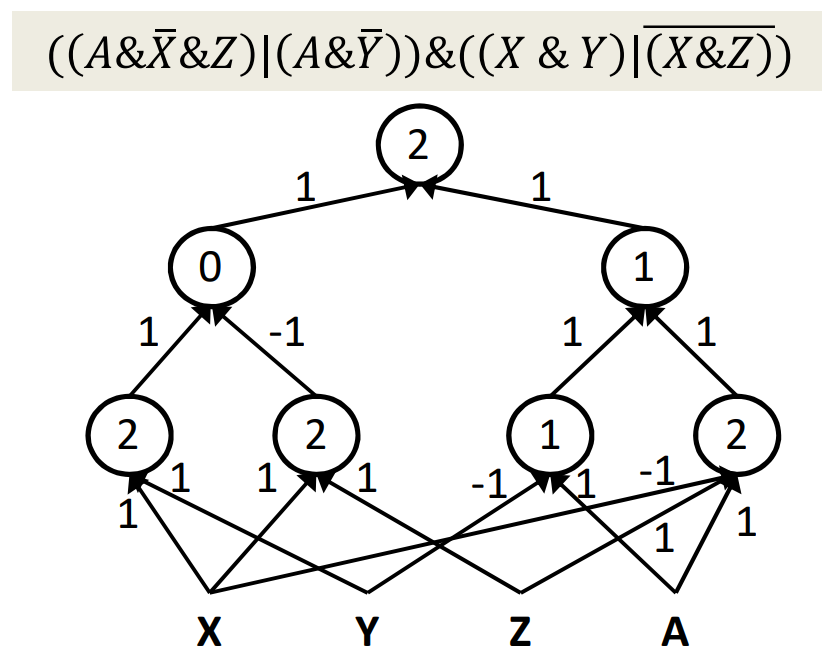
一个多层的感知机(“multi-layer preceptron”)可以表示任意复杂的布尔表达式,但是对于人的大脑来说输入并不是布尔的,现实生活中不是所有的输入都是布尔的。
The perceptron with real inputs
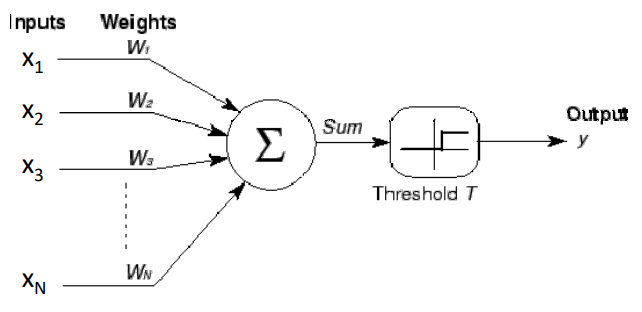
- $x_1, x_2, x_3…x_N$ 是输入的实数
- $w_1, w_2, w_3…w_N$ 也是实数
- $\sum_ix_iw_i>T$神经元被激活(这边的输出也是布尔的)
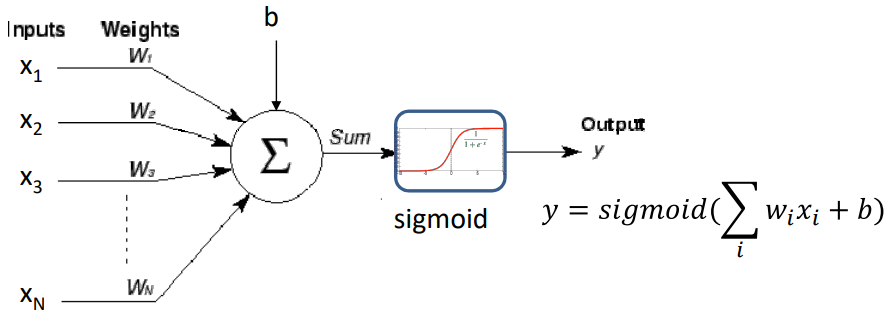
如图当激活函数不是阶跃函数的时候,输出可以是实数,上图sigmoid的输出可以看做是概率值。
- Any real-valued “activation” function may operate on the weighted sum input(Output will be real valued)
- The perceptron maps real-valued inputs to real-valued outputs
A Perceptron on Reals
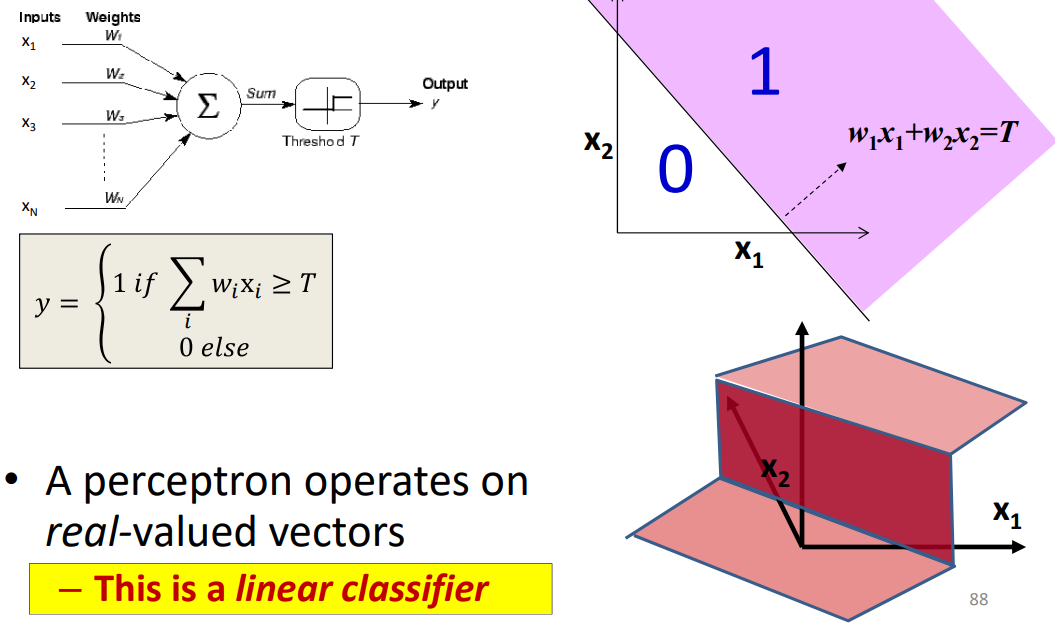 当感知机作用在实数空间的时候,是一个线性的分类器。
当感知机作用在实数空间的时候,是一个线性的分类器。
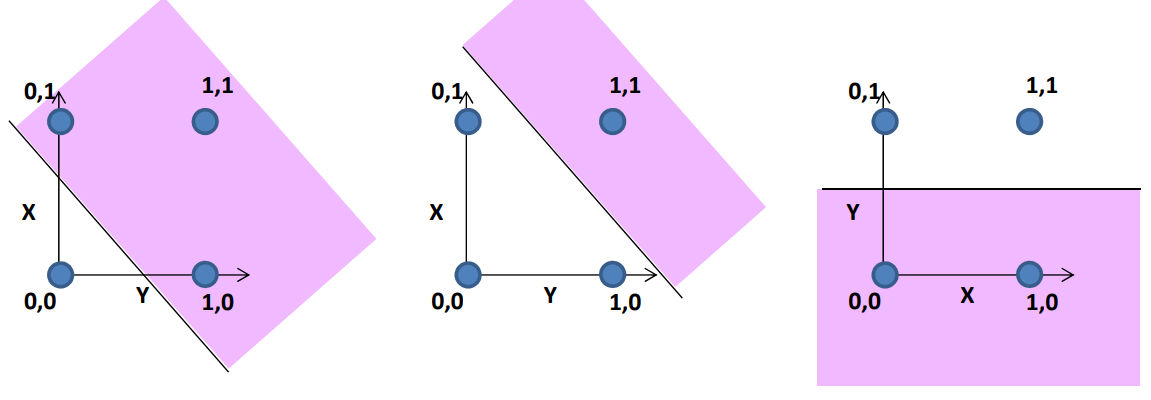
布尔类型的感知机模型是线性的,在上图的紫色区域的输出为1,这些平面可以通过设置特定的权重w和阈值t来实现。
Composing complicated “decision” boundaries
通过上述简单的分类边界可以组成复杂的分类边界,如图所示,我们可以将上述的分类边界进行组合来得到如图的五边形。
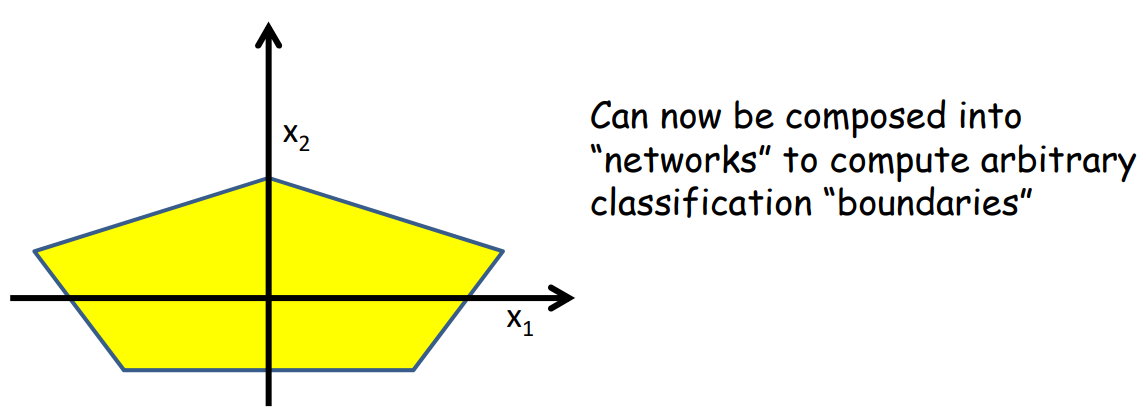
- Build a network of units with a single output that fires if the input is in the coloured area
Booleans over the reals
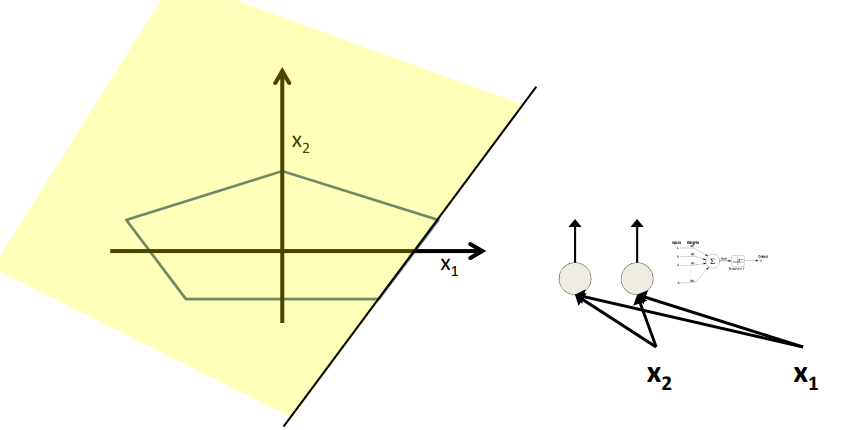
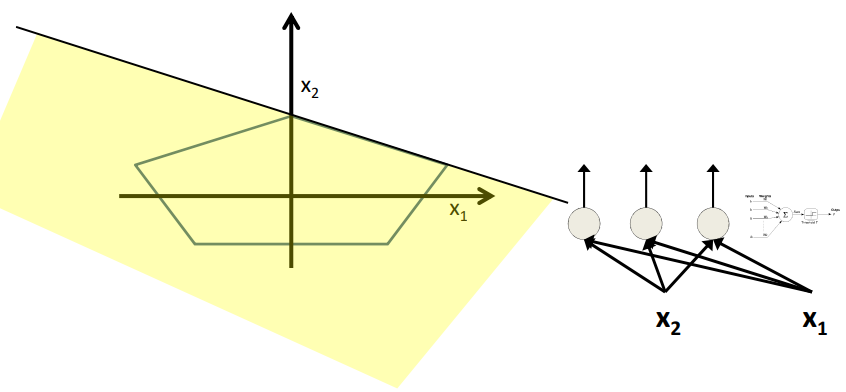
如图所示,每个感知机构成的线性边界组成了五边形的一个边。最后将这个五个边界再进行组合就可以构成五边形。
 |
 |
 |
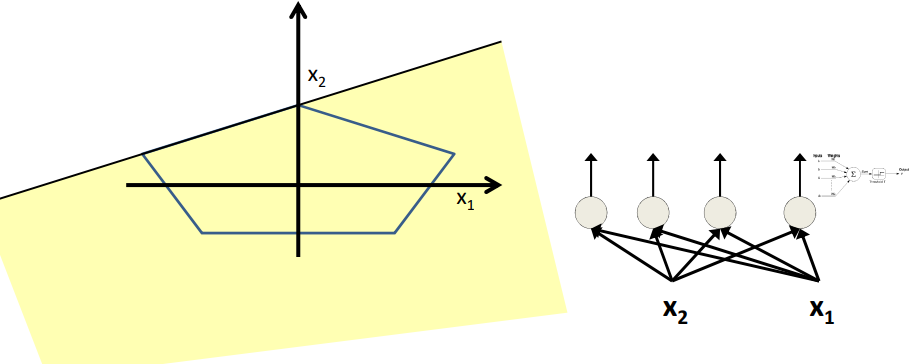 |
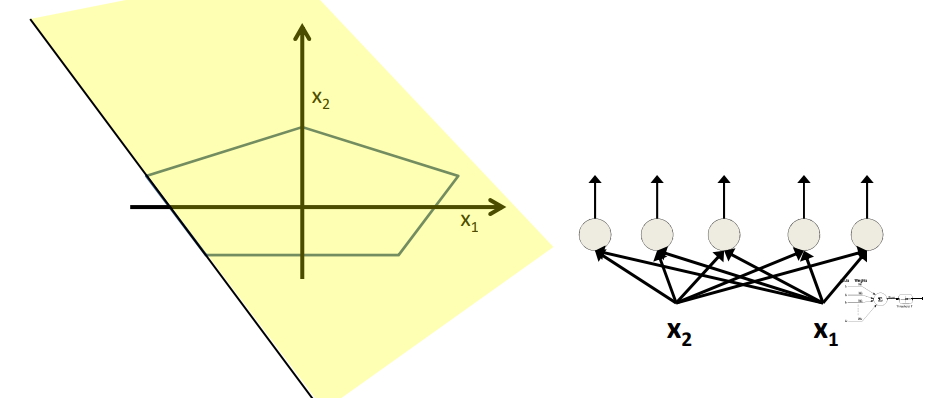
将上述的五个线性边界组合就可以得到如图所示的五边形。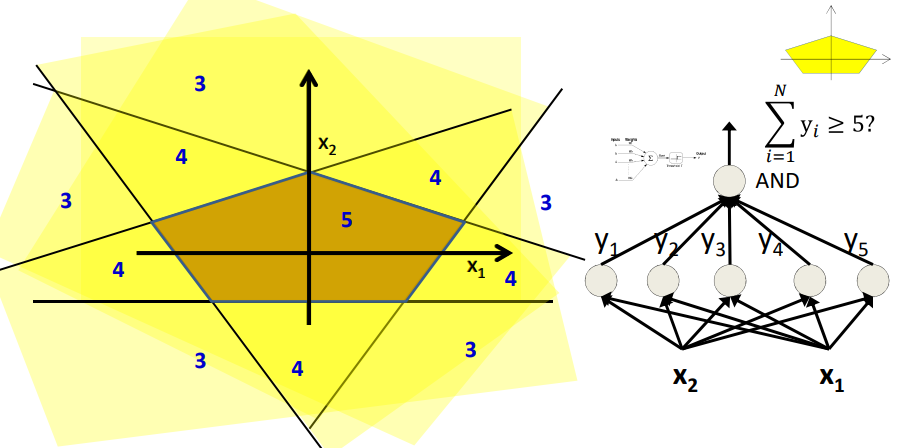
- The network must fire if the input is in the coloured area
More complex decision boundaries
将感知机组合可以得到更加复杂的决策边界。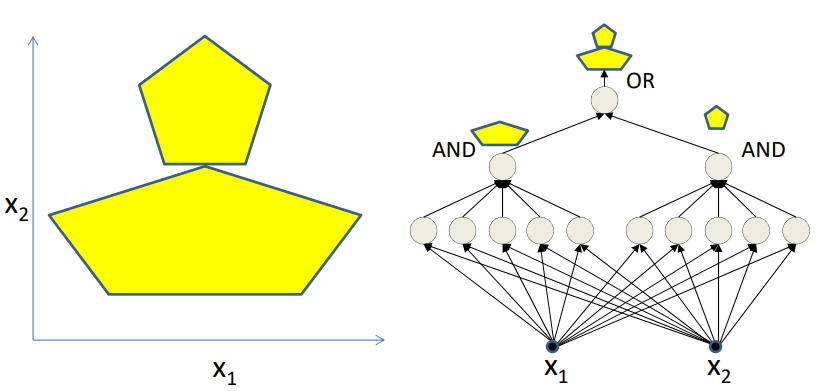
- Network to fire if the input is in the yellow area
- “OR” two polygons
- A third layer is required
综上相当于不同的神经元学习不同的边界(特征),更高层的神经元对底层的神经元进行组合来得到更加复杂的结果。
图中多变形的每个边界通过感知机来得到,然后将这些边界进行组合来得到复杂的多边形边界。
MLP as a continuous-valued regression

上面讲述的输出都是布尔类型的,感知机是否可以模拟连续出,老师给出的答案是可以,如下图所示,通过三个感知机可以模拟脉冲信号。
- A simple 3-unit MLP with a “summing” output unit can generate a “square pulse” over an input
- Output is 1 only if the input lies between $T_1$ and $T_2$
- $T_1$ and $T_2$ can be arbitrarily specified
感知机通过这种方式可以表示任意大小的脉冲,当$T_1$和$T_2$之间足够小的时候就可以表示一个点,如图通过将无数个这样的感知机组合可以模拟连续的输出。
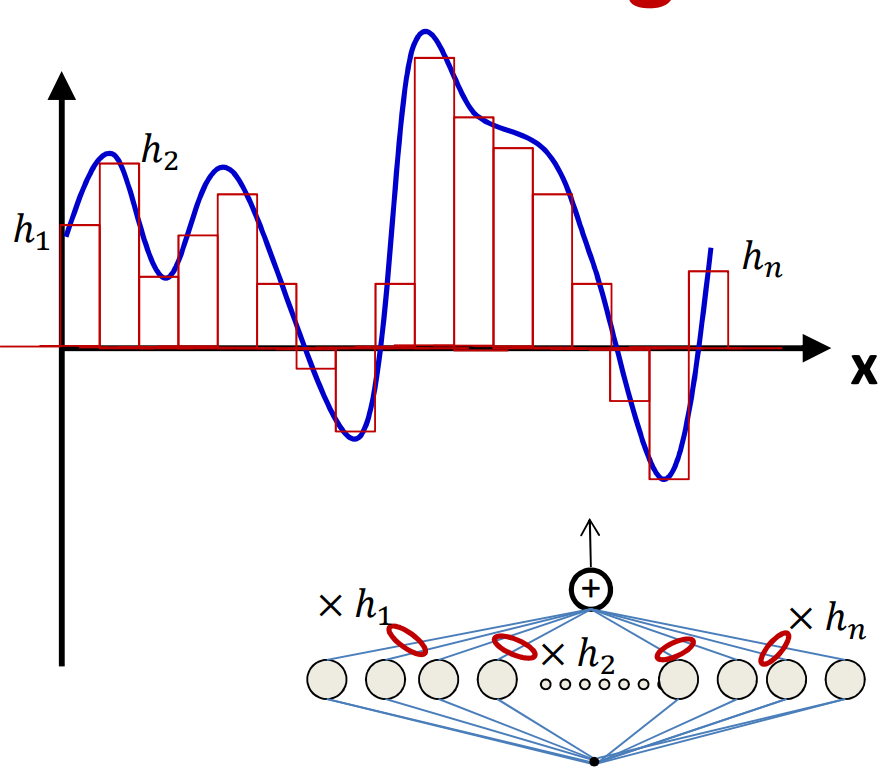
- An MLP with many units can model an arbitrary function over an input
- To arbitrary precision (Simply make the individual pulses narrower)
- This generalizes to functions of any number of inputs (next class)
对上述的阐述进行总结可以得到以下的结论。
- MLPs are connectionist computational models
- Individual perceptrons are computational equivalent of neurons
- The MLP is a layered composition of many perceptrons
- MLPs can model Boolean functions
- Individual perceptrons can act as Boolean gates
- Networks of perceptrons are Boolean functions
- MLPs are Boolean machines
- They represent Boolean functions over linear boundaries
- They can represent arbitrary decision boundaries
- They can be used to classify data
- Multi-layer perceptrons are connectionist computational models
- MLPs are classification engines
- They can identify classes in the data
- Individual perceptrons are feature detectors
- The network will fire if the combination of the detected basic features matches an “acceptable” pattern for a desired class of signal
- MLP can also model continuous valued functions
So what does the perceptron really model?
这一部分主要讲述对于感知机网络的一些直观的解释,对于后面神经网络的解释也有启发。
- Is there a “semantic” interpretation?
- What do the weights tell us?
- The neuron fires if the inner product between the weights and the inputs exceeds a threshold
- The neuron fires if the inner product between the weights and the inputs exceeds a threshold
老师给出的比较形象的结论是The weight as a $\color{red}{“template”}$
$X^TW > T$
$\cos \theta > \frac{T}{|X|}$
$\theta < \cos ^{-1}(\frac{T}{|X|})$
- The perceptron fires if the input is within a specified angle
of the weight - Neuron fires if the input vector is close enough to the weight vector
- If the input pattern matches the weight pattern closely enough
The weight as a template
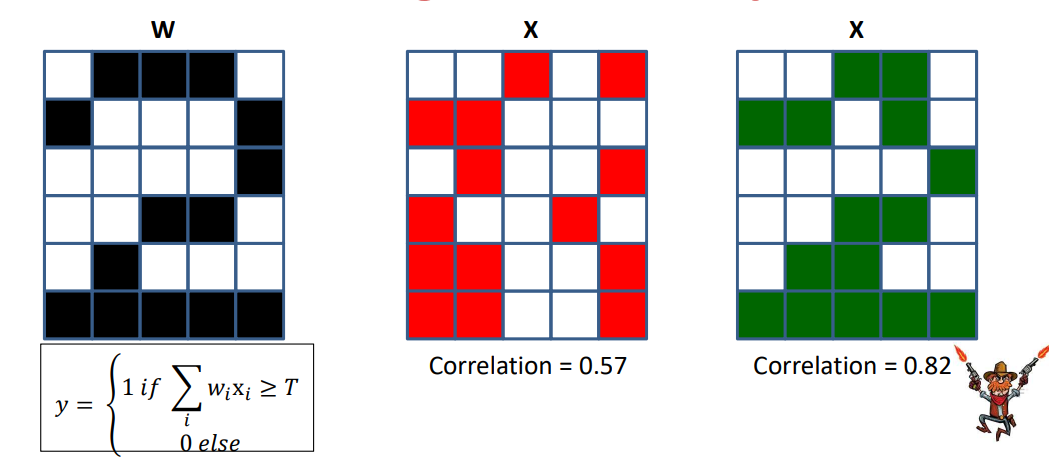
如果权重和输入的内积大于阈值,将会激活
- If the correlation between the weight pattern and the inputs exceeds a threshold, fire
- The perceptron is a correlation filter!
The MLP as a Boolean function over feature detectors
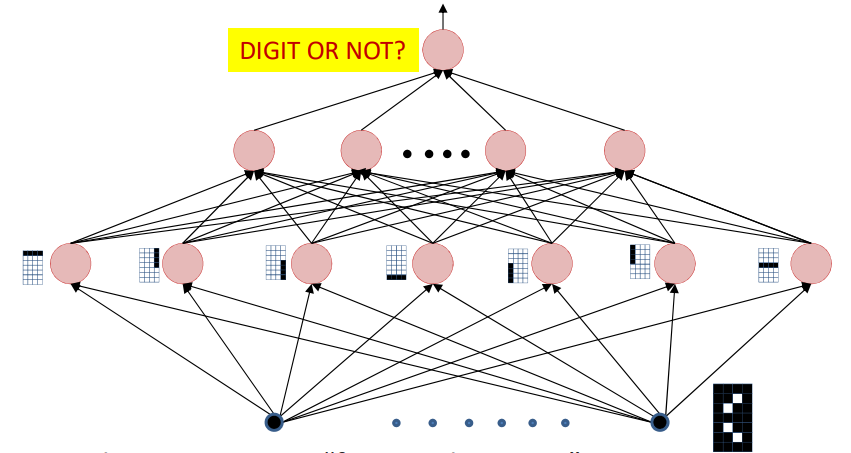
- The input layer comprises “feature detectors”
- Detect if certain patterns have occurred in the input
- The network is a Boolean function over the feature detectors
- I.e. it is important for the first layer to capture relevant patterns
The MLP as a cascade of feature detectors

- The network is a cascade of feature detectors
- Higher level neurons compose complex templates from features represented by lower-level neurons
- Perceptrons are correlation filters – They detect patterns in the input

